Source/Disclosures
Published by:
Disclosures:
Hudson reports no relevant financial disclosures. Please see the study for all other authors’ relevant financial disclosures.
In men with hypogonadism, there was no evidence that testosterone treatments cause short-term or medium-term CV risks, according to a meta-analysis published in The Lancet Healthy Longevity.
There were not enough data to conclude anything about the relationship between testosterone treatments and long-term CV risks, according to the researchers.

Source: Adobe Stock
“Prescribing of testosterone for hypogonadism is increasing globally, but conflicting messages about its safety may have led to many patients not receiving the treatment,” Jemma Hudson, MSc, from the Health Services Research Unit at the University of Aberdeen, United Kingdom, said in a press release. “Ongoing studies should help to determine the longer-term safety of testosterone, but in the meantime, our results provide much-needed reassurance about its short- to medium-term safety. Our findings could have important implications for the treatment of men with hypogonadism worldwide.”
Hudson and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 35 studies of trials of testosterone vs. placebo for hypogonadism including 5,601 participants (mean age, 65 years). Of those studies, 17 comprising 3,431 participants with a mean follow-up of 9.5 months had individual participant data. The researchers performed a one-stage meta-analysis of the individual participant data and a two-stage meta-analysis integrating individual participant data with the studies that did not provide it.
All-cause deaths were numerically lower in the testosterone group but were too few to determine statistical significance (0.4% vs. 0.8%; OR = 0.46; 95% CI, 0.17-1.24; P = .13), according to the researchers.
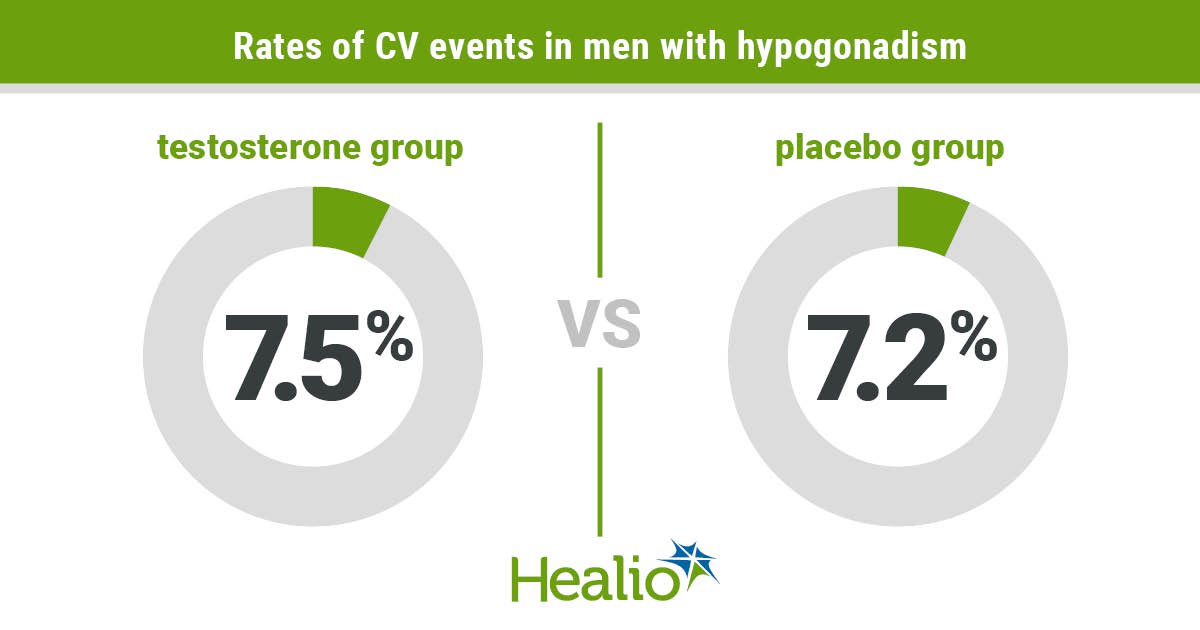
The rate of CV events was similar in both groups (testosterone, 7.5%; placebo, 7.2%; OR = 1.07; 95% CI, 0.81-1.42; P = .62), Hudson and colleagues wrote.
The most frequently occurring CV events were arrhythmia, CHD, HF and MI, all of which occurred at similar rates in both groups, according to the researchers.
There was no difference in CV risk by age (P for interaction = .17), baseline testosterone level (P for interaction = .69), smoking status (P for interaction = .35) and diabetes status (P for interaction = .025), the researchers wrote.
“An important strength of this [individual participant data] meta-analysis is its large size compared with individual testosterone trials, which have provided limited and situation-dependent information on cardiovascular safety,” Hudson and colleagues wrote. “This study has allowed us to more precisely estimate the incidence of cardiovascular events associated with testosterone treatment, which might be generalizable to patients worldwide.”
Reference:
- Little evidence testosterone treatment increases the risk of cardiovascular events, most in-depth analysis suggests. www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/954980. Published June 8, 2022. Accessed June 9, 2022.





